
MyURLMonitor Editorial
MyURLMonitor Editorial
How to Monitor Your Website’s Indexing Status
Google’s index is the gatekeeper to organic traffic. If your pages aren’t indexed, they don’t exist in search — and that can have serious business consequences. In fact, 62%1 of pages are never indexed, leading to lost visibility, traffic, and revenue. One e-commerce brand lost over $50,000/month when 200 product pages vanished due to a misconfigured plugin that added accidental noindex tags.
Whether you’re managing a blog, SaaS platform, or enterprise e-commerce store, staying indexed isn’t a bonus — it’s a requirement for growth. But as your site scales, manual indexing checks become inefficient, inconsistent, and risky.
This guide will show you how to shift from reactive fixes to proactive indexing management. You’ll learn:
- How to run manual indexing checks using tools like Google Search and Google Search Console
- How to dig deeper with advanced monitoring techniques like log file analysis and crawl budget optimization
- How to scale with automated monitoring tools like MyURLMonitor
- How top brands catch and fix de-indexing fast using real-world workflows and real world examples
- How continuous indexing insights lead to better SEO performance, content ROI, and long-term growth
| 📈 Key Stat: Sites using automated tools like MyURLMonitor recover from de-indexing 74%2 faster than those relying solely on manual checks. |
Let’s dive in — and make sure your most valuable pages stay indexed, discoverable, and driving results.
Part 1 - Manual Indexing Checks (for Small Teams & Quick Wins)
Before jumping into advanced analytics or enterprise tools, it’s important to master the basics. Manual indexing checks are a powerful way to spot problems early — especially for smaller websites or teams without access to SEO engineers or automation tools.
These free methods give you direct insights into how (or if) Google is indexing your content. You can quickly verify if new blog posts, landing pages, or product URLs are showing up in search results — and troubleshoot why they might not be.
That said, manual checks have real limitations. They’re time-consuming, offer no historical data, and quickly become unmanageable once your site grows past 100–500 URLs. Worse, relying solely on manual methods can delay detection of indexing issues for days or weeks — costing traffic, rankings, and revenue.
This part walks through the most reliable manual tools: the site: operator and Google Search Console. While these methods are great starting points, we’ll also show you where they fall short — and how automation tools like MyURLMonitor can fill the gaps before they become SEO disasters.
1.1 Using Google Search’s site: Operator
One of the quickest ways to check if your content is indexed is using Google Search directly via the site: search operator. It’s simple, accessible to anyone, and doesn’t require technical setup or login access.
Step-by-Step Guide
Basic Check:
- Visit Google.com
- Type
site:yourdomain.com(e.g.,site:myurlmonitor.com). - Review the results to see what pages are indexed
Advanced Filtering:
- Specific URL:
site:yourdomain.com/products - By Keyword in Title:
site:yourdomain.com intitle:"action camera" - By Year:
site:yourdomain.com 2025
What the Results Mean
- Listed = Indexed
- If key URLs (e.g.,
/pricing,/blog/new-post) are missing, they may have indexing issues
Limitations
- Google displays only up to ~1,000 results regardless of your actual page count
- Results may include cached or outdated pages, not real-time data
- Some URLs may appear indexed but are not actively crawled or displayed in search
To verify accuracy, you can also use cache:yourdomain.com/url to view Google’s last version. This shows the most recent version of the page stored by Google.
✨ Real-World Example: A travel blogger couldn’t find their new post using the site: operator. After checking with GSC’s URL Inspection Tool, they discovered their CMS plugin had accidentally added a noindex tag. Once removed, the post reappeared in search results within 48 hours. |
1.2 Google Search Console (GSC)
While site: search is fast, it lacks precision. Google Search Console (GSC) offers verified, page-level insights directly from Google, making it the go-to tool for manual indexing diagnostics.
GSC is ideal for:
- Website owners with verified domains
- SEO professionals conducting in-depth audits
- Anyone wanting to understand why a page isn’t indexed
1.2.1 Index Coverage Report
How to Use It:
- Go to GSC > Indexing > Pages
- View the chart: Indexed vs. Excluded
- Click "Excluded" to reveal specific reasons
Common Exclusion Reasons:
- Crawled - Currently Not Indexed: May signal duplicate, low-quality, or thin content
- Blocked by robots.txt: Robots file is disallowing the page
- Duplicate - Google chose different canonical: Google selected another page to represent the content
What to Do:
- Prioritize high-value excluded URLs (product pages, blog hubs)
- Export to CSV for filtering
- Cross-reference with Google Analytics to see if excluded pages used to drive traffic
1.2.2 URL Inspection Tool
How to Use It:
- Enter full URL in the top bar (e.g.,
https://yourdomain.com/page) - Click Test Live URL
- Review result:
- “URL is on Google”: Good
- “URL is not on Google”: Investigate error
Common Errors & Fixes:
- Blocked by robots.txt: Edit or remove the disallow rule
- Duplicate without canonical: Add a self-referencing canonical:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://yourdomain.com/page">
⚠️ Limitations:
- Can only inspect one URL at a time
- Doesn’t show historical changes or alert you when something is de-indexed
1.3 Weekly Manual Monitoring Workflow
For smaller sites, a consistent manual check routine can be effective. Here’s how to combine the tools:
Weekly Audit Steps:
- Use
site:operator for a high-level scan - Dive deeper with GSC’s Index Coverage Report
- Investigate key pages using the URL Inspection Tool
| ✨ Real-World Example: An online course platform runs this workflow weekly. They ensure new course pages are indexed, troubleshoot excluded content, and optimize seasonal landing pages using canonical tags. |
1.4 When to Move Beyond Manual Methods
Manual monitoring is a great start, but it's only sustainable for smaller websites. If you find yourself spending hours each week checking URLs, or if your site has hundreds (or thousands) of pages, it's time to consider automation.
Signs You’ve Outgrown Manual Checks:
- Your site has 100-500 pages or more
- You’re spending 2+ hours/week on indexing checks
- You want to track indexing trends over time
- You need alerts when critical pages drop
This is where tools like MyURLMonitor come in. With real-time alerts, priority tagging, bulk URL tracking, and Indexing API integration, MyURLMonitor gives you back hours of time while catching issues faster and more reliably than manual checks ever could.
Next up: Learn how log file analysis and automated tools unlock even deeper indexing insights in Part 2.
Next: Learn advanced techniques like log file analysis and enterprise tools in Section 2.
Part 2 - Advanced Monitoring Techniques (for Scaling Teams & SEO Pros)
As your site grows, so does your risk. Manual methods break down quickly when you’re publishing content daily, managing thousands of URLs, or operating across multiple domains. Part 2 explores advanced indexing analysis tools and workflows that help SEO professionals stay proactive and efficient.
Whether you manage an enterprise news site or a fast-scaling SaaS product, the following strategies will help you:
- Diagnose crawl vs. index issues
- Understand how Googlebot behaves on your site
- Proactively resolve indexing problems using automation and AI
We’ll also cover real-world examples of how teams are combining tools like log analyzers and MyURLMonitor to prevent traffic loss and maximize organic visibility.
Let’s dive in.
2.1 Log File Analysis
Log file analysis lets you see exactly how search engines interact with your website. Unlike tools that show what's indexed, logs reveal what's crawled — including pages that might never make it into Google’s index.
This technique is especially useful for:
- Diagnosing crawl budget inefficiencies
- Identifying pages that are crawled but not indexed
- Spotting duplicate content or parameter issues
Getting started
- Access Server Logs
- Shared Hosting: cPanel > Metrics > Raw Access Logs
- Cloud Hosting: AWS CloudWatch or log exports from S3
- Filter for Googlebot
- Use tools like Screaming Frog Log Analyzer
- Filter user-agent:
Googlebot
- Analyze Crawl Patterns
- Which pages are crawled often but still not indexed?
- Are low-value pages (e.g.,
/tag/,/filter=...) wasting crawl budget?
Advanced Tip:
Compare logs with GSC index data. Look for pages that are frequently crawled but excluded from the index. These often require content fixes, canonical adjustments, or redirects.
✨ Real-World Example: A SaaS company found that its /features/page was crawled 15 times per month but wasn’t indexed. Adding unique testimonials and case studies helped it index and rank. |
2.2 Automated Monitoring Tools (Like MyURLMonitor)
Manual checks and logs are valuable, but not scalable. Automated tools like MyURLMonitor allow SEO teams to track thousands of pages across websites in real time.
Key Benefits:
- Track index status for 10K+ URLs
- Get fast alerts for pages that were de-indexed — detected within 24 hours
- Access historical trends
- Detect canonical conflicts or 404s
2.3 Hybrid Monitoring Strategies
The best results often come from combining log file insights with automated monitoring.
Hybrid Workflow Example:
- Analyze logs to detect pages frequently crawled but unindexed
- Tag those pages as "high priority" in MyURLMonitor
- Receive real-time alerts if they drop from the index
- Trigger automated fixes via Zapier or in CMS
This approach blends depth and speed, helping you catch and fix indexing problems before they affect traffic.
2.4 Monitoring JavaScript-Heavy Pages
If your site runs on React, Vue, or Angular, indexing issues can be hard to detect.
Common Problems:
- Client-side rendering: Content isn’t visible to Googlebot
- Infinite scroll or faceted filters create bloated URL sets
Solutions:
- Use pre-rendering or dynamic rendering for bots
✅ Ready to protect your indexing and revenue?
Sign up to be the first to know when we launch — and get exclusive early access discounts.
![]()
Part 3 - Setting Up MyURLMonitor for Automated Indexing Checks
If you’ve reached this point, you’ve likely realized that manual monitoring alone can’t keep up. Part 3 is your hands-on guide to setting up MyURLMonitor, a scalable indexing monitoring solution designed to help you stay ahead of problems — not just react to them.
Whether you manage a blog, an e-commerce site, or a sprawling enterprise CMS, you’ll learn how to:
- Install and configure MyURLMonitor
- Link your websites to MyURLMonitor to start the automation for indexing requests
- If needed, add URLs manually to monitor
- Do simple troubleshooting
- Maintain your setup
Let’s walk through it step by step, but first a reminder of why it is so important.
3.1 Why Indexing Automation Matters
Once your site grows beyond 100 pages or starts publishing frequently, manual checks are not just inefficient — they’re risky.
Benefits of Automating with MyURLMonitor:
- Save time: What used to take hours now takes minutes
- Improve accuracy: Eliminate human error in tracking index status
- Enable faster fixes: Detect issues early with real-time alerts
- Track performance over time: Understand long-term trends with historical data
| ✨ Real-World Example: An e-commerce site with over 5,000 product pages reduced indexing errors by 80%3 after automating checks through MyURLMonitor, recovering $22K/month3 in lost revenue. |
3.2 Step-by-Step Setup Guide
Step 1: Sign in with your Google Search Console Account
- Visit https://myurlmonitor.com/login and select Google Login
- Use your Google Search Console Account to log in.
Step 2: Choose your MyURLMonitor plan
- Starter: $15.99 per month, billed annually – 3 websites, 400 pages per day
- Pro: $28.99 per month, billed annually – 10 websites, 2 team seats, 800 pages per day
- Business: $53.99 per month, billed annually – 20 websites, 5 team seats, 1,200 pages per day, priority support
- Agency: $103.99 per month, billed annually – 50 websites, 10 team seats, 2,000 pages per day, priority support
Once your transaction is successful, you will automatically be redirected to your Dashboard.
Step 2: How to Grant Access and View Indexing Status in MyURLMonitor
MyURLMonitor will automatically detect all the domains and websites associated with your Google Search Console account, and show these in your dashboard.
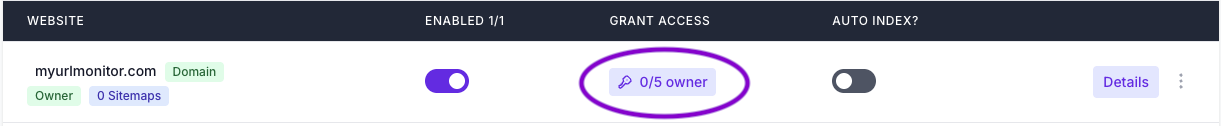
-
In the Sites overview, click the button under Grant Access “0/5 owner”.
-
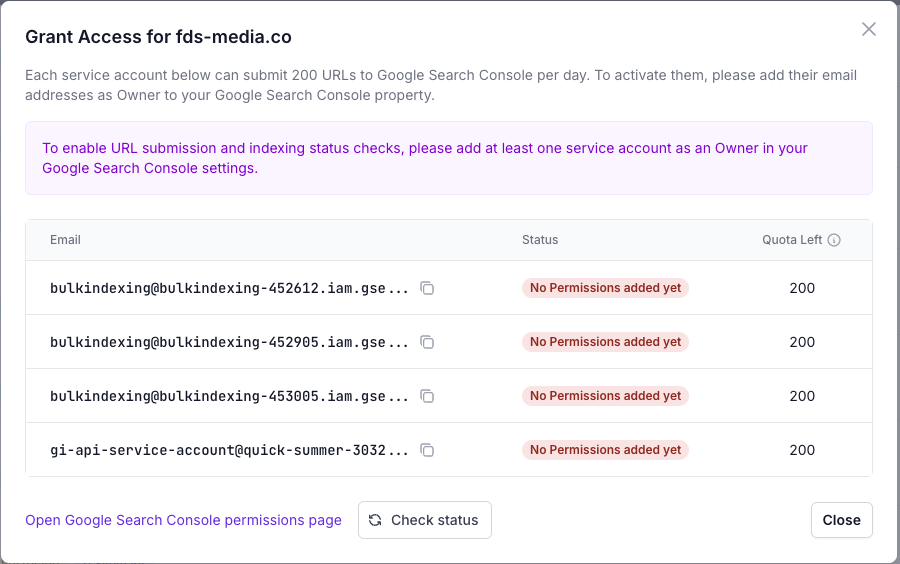
A mini window called “Grant Access” will open, showing a list of service accounts linked to your customer account.
-
Copy at least one of the service email addresses listed.
-
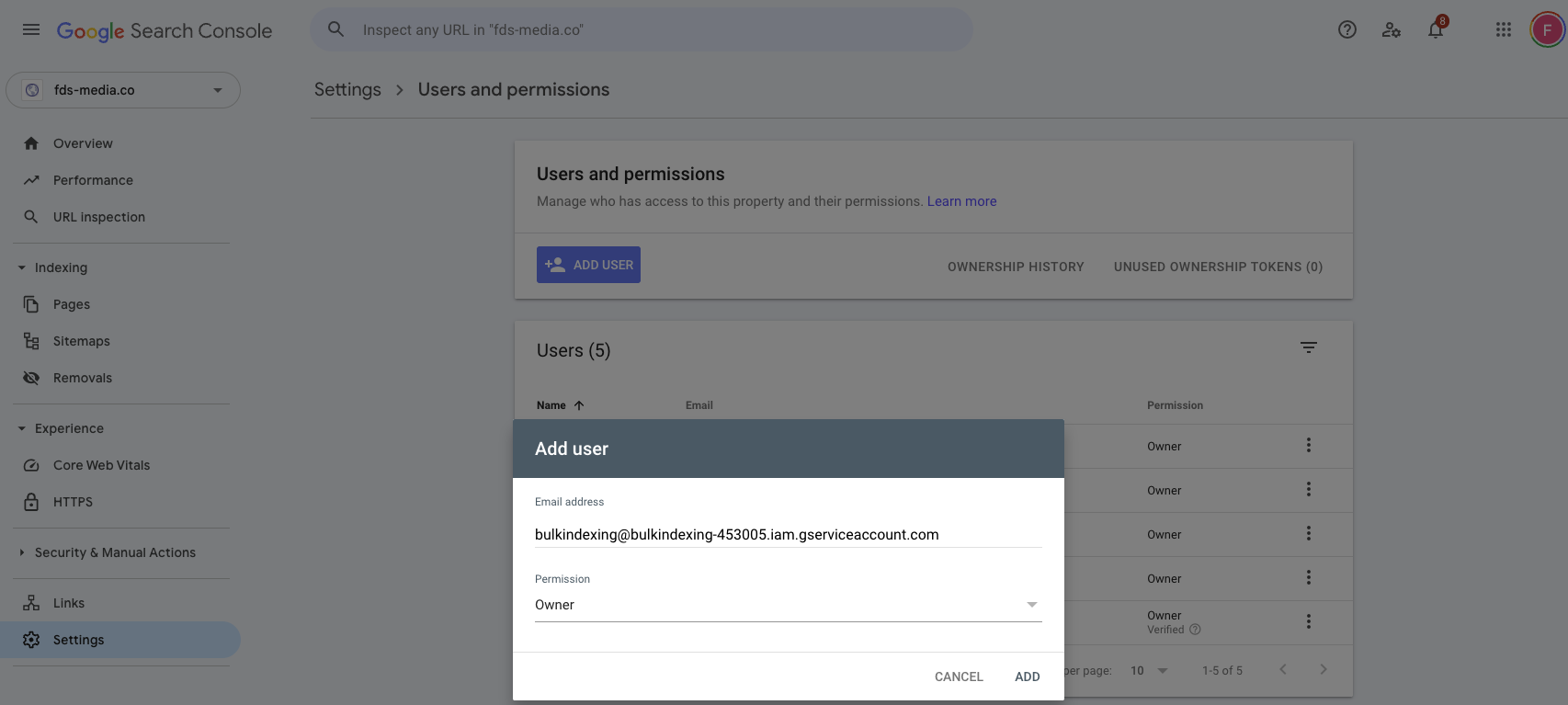
In a new tab, go to Google Search Console (GSC) > Settings > Users and Permissions.
-
Add the copied email as a Permission Owner in GSC.
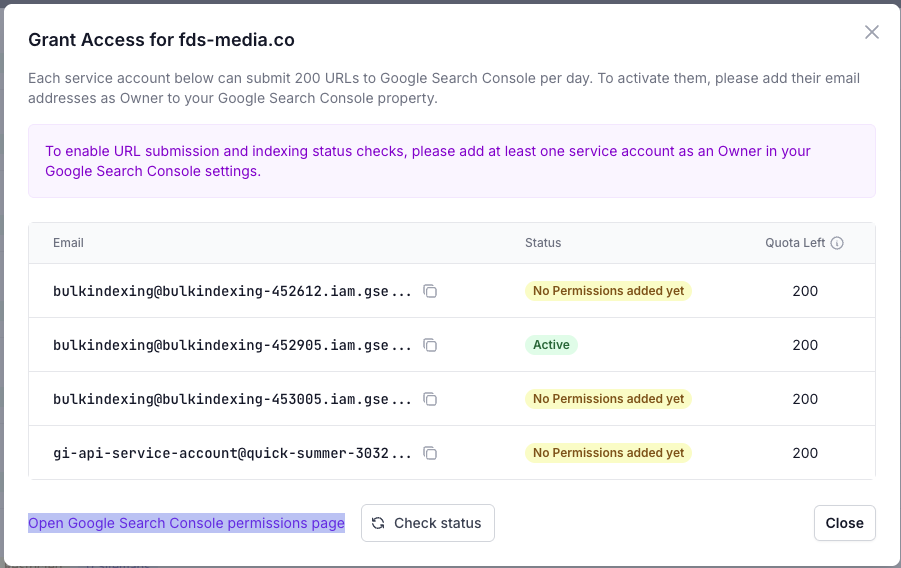
- Return to the open “Grant Access” window and click “Check Status”.
- You’ll see a message saying “Checking service account permissions…” as the system verifies access for all service accounts.
What Happens Next
- Once the system confirms that at least one service account now has OWNER permissions, it automatically retrieves the website’s sitemaps from Google Search Console.
- If it finds an index or meta sitemap, it will also collect all listed child sitemaps.
- From each sitemap, the system extracts page URLs only (image URLs are ignored).
- It then retrieves the indexing status for up to 2,000 URLs at a time, depending on how many pages your site has.
- The results are saved and displayed in your dashboard, giving you insight into which pages are indexed and which are not.
Option 1: Prioritize URLs by uploading them
- If you want, use Screaming Frog or site audit tools to export a list of URLs that you would like to prioritize
- Copy and paste these URLs into the Add pages option in the Site Details
Option 2: Sitemap Sync
- Submit your XML sitemap to Google Search Console as usual
- MyURLMonitor will auto-discover and track new URLs in this new sitemap.
3.3 Troubleshooting Common Issues
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| URLs Not Detected | Check robots.txt isn’t blocking crawlers. |
| Crawled - Currently Not Indexed | May signal duplicate, low-quality, or thin content, fix by improving content quality |
| Discovered - Not Indexed | Use a MyURLMonitor to automate indexing requests, analyse crawl budget issues, improve content quality, add internal links, and get more good backlinks. |
| Blocked by robots.txt | Robots file is disallowing the page, review and fix your robots.txt file |
| Duplicate - Google chose different canonical | Google selected another page to represent the content |
3.4 Maintaining Your Setup
To keep things running smoothly:
- Audit monthly: Review dropped URLs
- Adjust seasonally: Add temporary landing pages to tracking
💡Pro Tip: Use the "Index Health Score" feature in your dashboard to measure your quarterly indexing progress and site reliability.
Next: In Part 4, we’ll explore the long-term strategic SEO benefits of continuous monitoring, from preventing costly traffic loss to saving time and resources.
Part 4 - Strategic SEO Benefits of Continuous Indexing Monitoring
Now that you’ve set up automated indexing monitoring, let’s explore the bigger picture. Part 4 unpacks how continuous monitoring can become a strategic advantage — not just a technical safety net.
By staying on top of indexing health, you don’t just prevent disasters — you make smarter decisions, improve ROI, and strengthen your long-term SEO infrastructure.
4.1 Prevent Costly Traffic Loss
Google’s index is volatile. Pages can disappear overnight due to technical errors, algorithm updates, or CMS misconfigurations. Without monitoring, you may not notice until rankings and revenue are already lost.
Time-to-Detect Comparison:
- Manual checks: ~14 days (avg.)
- MyURLMonitor alerts: ~2 hours
Core Update Recovery
During Google updates, visibility shifts rapidly. With monitoring, you can:
- Identify pages affected by algorithm changes
- Prioritize recovery efforts based on traffic impact
- Spot thin content, duplicate pages, or outdated sections
4.2 Save Time and Resources
Manual checks are slow and error-prone. MyURLMonitor automates repetitive tasks so your SEO team can focus on strategy.
| Task | Manual | MyURLMonitor |
|---|---|---|
| Check 1,000 URLs | 8 hours | 5 minutes |
| Diagnose root-cause | 2 hrs/page | Instantaneous |
| Weekly reporting | 3 hrs/week | Available on demand |
Annual savings = 500+ hours for sites with 10,000+ pages.
Resource Reallocation: Use saved time for high-impact work:
- Technical audits
- Content updates
- Link-building and outreach
4.3 Summary
Continuous indexing monitoring isn’t just about technical hygiene — it’s about:
- Protecting traffic from unpredictable drops
- Unlocking strategic SEO growth via smarter insights
- Maximizing ROI on every piece of content
- Scaling workflows across teams and tools
Whether you're running a lean in-house SEO team or managing SEO for global brands, automated indexing insights give you the control and confidence to grow your visibility and performance.
Ready to level up your monitoring?
👉 Sign up to get early access to MyURLMonitor and receive exclusive launch discounts.
Get Early Access

